Egg fertilisation
The fundamental step to initiate embryonic development
IVF (In Vitro Fertilisation)
Conventional in vitro fertilisation (IVF) is ideal for couples where the semen analysis is normal and an adequate number of eggs is available.
After ovarian puncture, your partner’s sperm is processed in our laboratory and placed together with the eggs under optimal conditions that replicate the natural environment of the human body.
Twenty-four hours later, an embryologist examines the eggs under a microscope to confirm whether fertilisation has taken place. The fertilisation rate is usually between 50% and 70%, depending on the quality of both the sperm and the eggs.
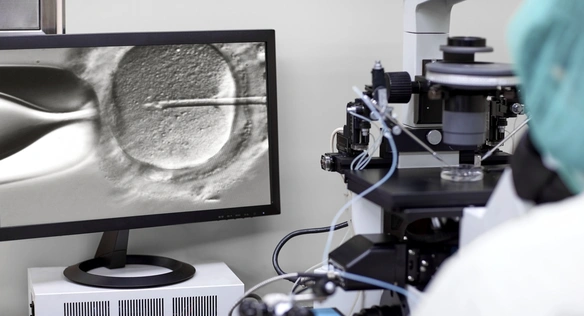
ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection)
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) is one of the most effective techniques in modern assisted reproduction.
During the procedure, the highest quality sperm is selected using advanced methods and injected directly into the egg.
This makes it possible to overcome multiple barriers in the fertilisation process and significantly increases the chances of success.
We recommend ICSI in the following cases:
- When the semen analysis shows a low sperm count, reduced motility, or abnormal morphology
- If a previous IVF cycle did not result in fertilisation
- When only a small number of eggs have been retrieved
- In cases where frozen sperm is used
- If the sperm has been obtained through surgical extraction (TESE)
- When donor eggs are used
- In other situations, as determined by medical judgement
Frequently asked questions about egg fertilisation
What is egg fertilisation?
Fertilisation is the process by which a sperm penetrates an egg, resulting in the formation of an embryo. It can occur naturally in the fallopian tubes or in a laboratory through assisted reproduction techniques.
How long does fertilisation take?
After ovulation, the egg can be fertilised within approximately 12 to 24 hours. In assisted reproduction, this process is monitored in the laboratory in the hours following the collection of eggs and sperm.
What are the requirements for natural fertilisation to occur?
A mature egg, a functional sperm cell, and an appropriate environment in the fallopian tubes are necessary. Other influencing factors include semen quality, ovulation, and the health of the fallopian tubes.
What is the difference between natural and assisted fertilisation?
In natural fertilisation, the meeting of egg and sperm takes place inside the body. In assisted fertilisation (such as IVF or ICSI), the process occurs in the laboratory with the aim of increasing the chances of pregnancy.
Can symptoms be detected when an egg has been fertilised?
There are no immediate symptoms. The first changes usually appear several days later, when the embryo begins implantation. At that point, light spotting, tiredness, or breast tenderness may occur.
What happens if the egg is not fertilised?
If fertilisation does not occur, the egg degenerates and is naturally expelled with menstruation. In assisted reproduction, if fertilisation does not take place in the laboratory, the cause is analysed and additional techniques such as intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be recommended.
How is fertilisation verified in an IVF treatment?
Between 16 and 18 hours after insemination of the egg, embryologists check in the laboratory whether fertilisation has occurred by observing the presence of pronuclei (structures indicating that the genetic material of the egg and the sperm has combined).
What factors can hinder egg fertilisation?
Some of the most common factors include poor egg quality, abnormalities in sperm, advanced maternal age, fallopian tube problems, or hormonal imbalances.