
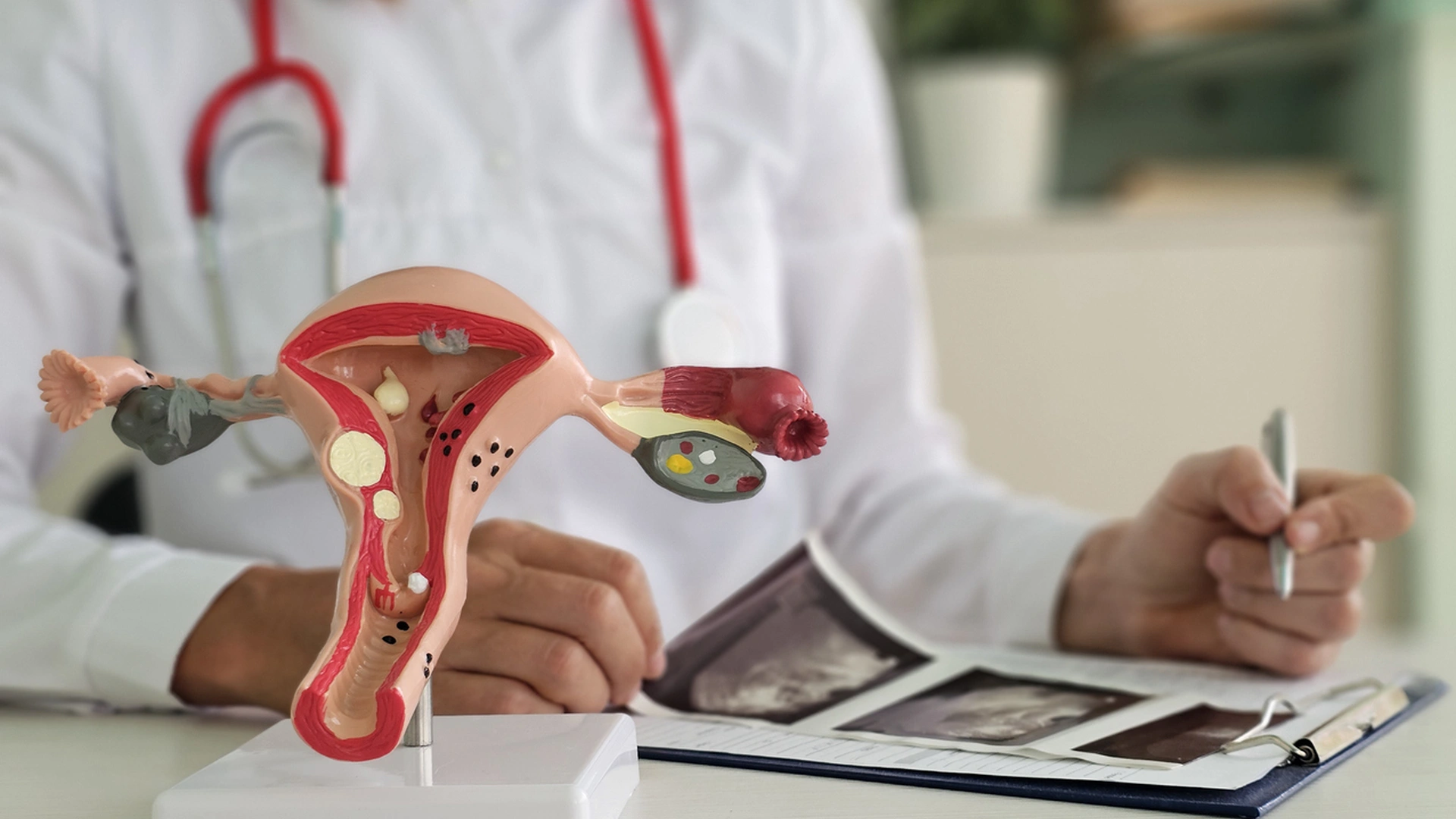
Hydrosalpinx is an alteration of the fallopian tubes that involves the accumulation of fluid, leading to their dilation and obstruction. The fluid buildup and blockage prevent the tubes from functioning normally and carrying out their roles.
The fallopian tubes are structures connected to the uterus that collect the egg at the time of ovulation. Within the tubes, the egg can be fertilized and then transported into the uterine cavity.
Main causes of hydrosalpinx
This fluid accumulation can have several causes. Some of the most common include:
- Infections: Pelvic infections, especially those caused by sexually transmitted bacteria such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can cause inflammation in the fallopian tubes. Chronic inflammation may lead to obstruction and fluid accumulation.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is a condition in which tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus begins to grow outside of it. If this tissue affects the fallopian tubes, it can cause blockages and fluid buildup.
- Previous pelvic surgeries: Surgical procedures in the pelvic region, such as gynecological or abdominal surgery, can lead to scarring and adhesions that interfere with the normal function of the fallopian tubes.
- Injuries or trauma: Pelvic trauma, whether from accidental injuries or medical procedures, can damage the fallopian tubes and result in scarring and obstruction.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID): PID is an infection of the female reproductive organs. If not properly treated, it can damage the fallopian tubes, leading to obstruction and fluid accumulation.
- Congenital abnormalities: Some women may be born with abnormalities of the fallopian tubes that increase the risk of hydrosalpinx.
- Contraceptive medical procedures: In rare cases, certain contraceptive procedures, such as tubal ligation, may lead to fluid accumulation in the fallopian tubes.
- Idiopathic factors: In some cases, the exact cause of hydrosalpinx cannot be identified and is classified as idiopathic when no obvious reason is found.
It is important to note that hydrosalpinx can be asymptomatic in its early stages, and some women may not be aware of the condition until they experience difficulties conceiving.
What are the symptoms of hydrosalpinx?
In most cases, hydrosalpinx is asymptomatic. However, in some women it may cause:
- Increased menstrual pain (dysmenorrhea).
- Intermenstrual bleeding (bleeding between periods).
- Most often, it is an incidental finding on a gynecological ultrasound.
Diagnostic tests for hydrosalpinx
Hydrosalpinx can be diagnosed using imaging techniques. On gynecological ultrasound, it may appear as thickening and dilation of the fallopian tubes. It can also be identified during a hysterosalpingography performed to assess tubal patency.
Another direct diagnostic method is laparoscopy, which allows direct visualization of the condition of the tubes.
Treatment for hydrosalpinx
In women who are trying to conceive, when hydrosalpinx is detected the recommended approach is surgical treatment to remove it.
The only effective option is to perform a salpingectomy of the affected tube. Salpingectomy is a relatively simple surgical procedure that can be done via laparoscopy, in which the fallopian tube(s) are partially or totally removed.
There are two main types:
- Unilateral salpingectomy: Only one fallopian tube is removed. This is generally performed when there is obstruction, damage or a specific condition affecting one tube. Removing the damaged tube may help improve fertility or address medical issues.
- Bilateral salpingectomy: Both fallopian tubes are removed during surgery. This may be recommended when hydrosalpinx affects both tubes.
In women with endometriosis or deep pelvic adhesions, the procedure may be more complex.
What happens if hydrosalpinx is not treated?
The purpose of this treatment is to prevent the toxic effect of the accumulated fluid on the endometrium. The fluid collects in the tubes, dilating them, and can spill into the uterine cavity, creating a hostile environment for embryo implantation and normal embryonic development.
Hydrosalpinx can reduce the chances of spontaneous pregnancy and, in the case of in vitro fertilization (IVF), it can lower implantation rates after embryo transfer.
For this reason, scientific societies specializing in assisted reproduction agree on the need to treat hydrosalpinx before IVF.
Hydrosalpinx and pregnancy
Because salpingectomy involves partial or total removal of the fallopian tubes, it has a significant impact on a woman’s ability to conceive naturally.
After a salpingectomy, the possibility of conceiving naturally is reduced, especially if both tubes are removed. However, it is important to note that in vitro fertilization (IVF) remains a viable option for many women who have undergone a salpingectomy. In IVF, eggs and sperm are combined in a laboratory and the resulting embryos are then transferred into the uterus.
Book a free consultationDo you have any questions or need more information?
At Fertility Madrid, we specialise in treatments such as egg donation, in vitro fertilisation and artificial insemination, among others.
Please do not hesitate to contact our professionals at our fertility clinic and they will answer all your questions without obligation.

Óscar Oviedo
Director Médico




